KirkPatrick-Seidel Algorithm
The kps algorithm is an efficient solution to the convex-hull problem,particularly in dealing with degenerate cases
(situations with collinear points or points with the same x-coordinate).It works by recursively dividing the points based on their x- coordinates and at each iteration it discards points that
cannot contribute to the convex hull by pruning the search space in this manner this algorithm is more efficient and
works on a better complexity.
The algorithm works as follows:
The set of points is divided into two sets by a median line .We then find all the edges of the convex-hull that
intersect the median line. We then proceed to remove points that cannot be a part of the convex-hull.we then recursively
call the algorithm on the reduced search space.
DIVIDE AND CONQUER:
It is a class of algorithms where the problem is broken down into smaller sub-problems, do this recursively until the
subproblem can be solved directly. We then merge the solutions of the subproblems to get the solution to the original
problem.in most cases the divide and conquer approach is able to achieve a better time complexity solution than
algorithms that solve the problem at once.
MEDIAN OF MEDIANS:
The algorithm divides a given dataset into small groups(typically groups of 5) and uses a simple sorting algorithm like
bubble sort to sort the sub-group and then get the median of the sub-group ,it then treats the set of medians of
subgroups as a new set and call the algorithm recursively on this new set.in this way we find the median of medians and
this algorithms finds the median of a set of n points in O(n).
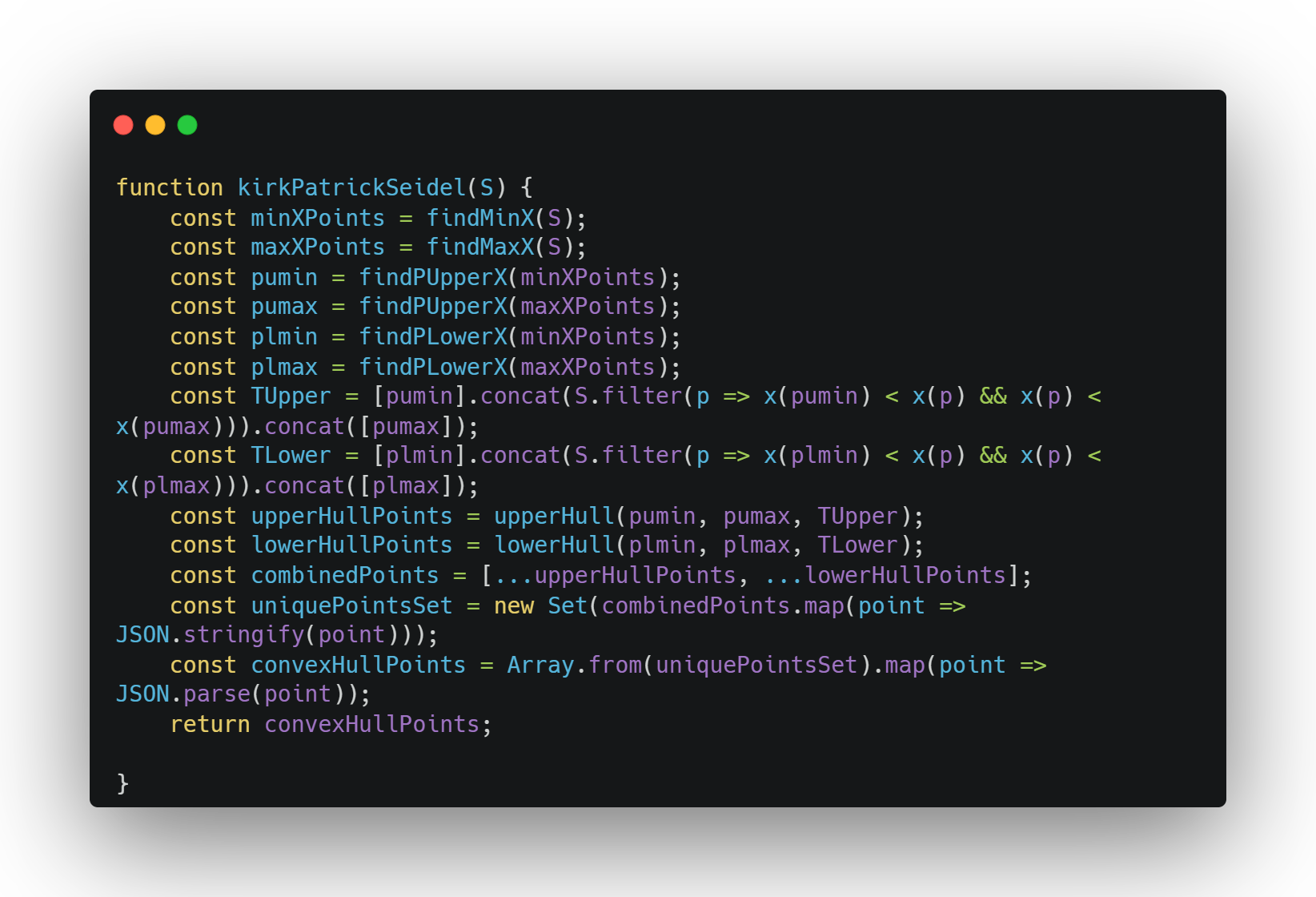
KirkPatrick-Seidel Main Function
This is the main function of the code and the parameter S that we pass is the set of points for which we wish to find the convex hull and the function returns the set of points that form the convex hull for the given input. It begins by finding the points with the highest and lowest x-coordinate using the helper functions finMinX and findMaxX. It then builds the sets of points for the upper and lower hulls by considering the x-coordinate of each point relative to the median x-coordinate using the helper functions Tupper and Tlower. It recursively calls upperHull and lowerHull on these sets of points to find the upper and lower hulls respectively. The function finally combines the sets of points obtained from both the hulls respectively and returns the final answer after concatenating them and removing any duplicates.
Upper Hull Function
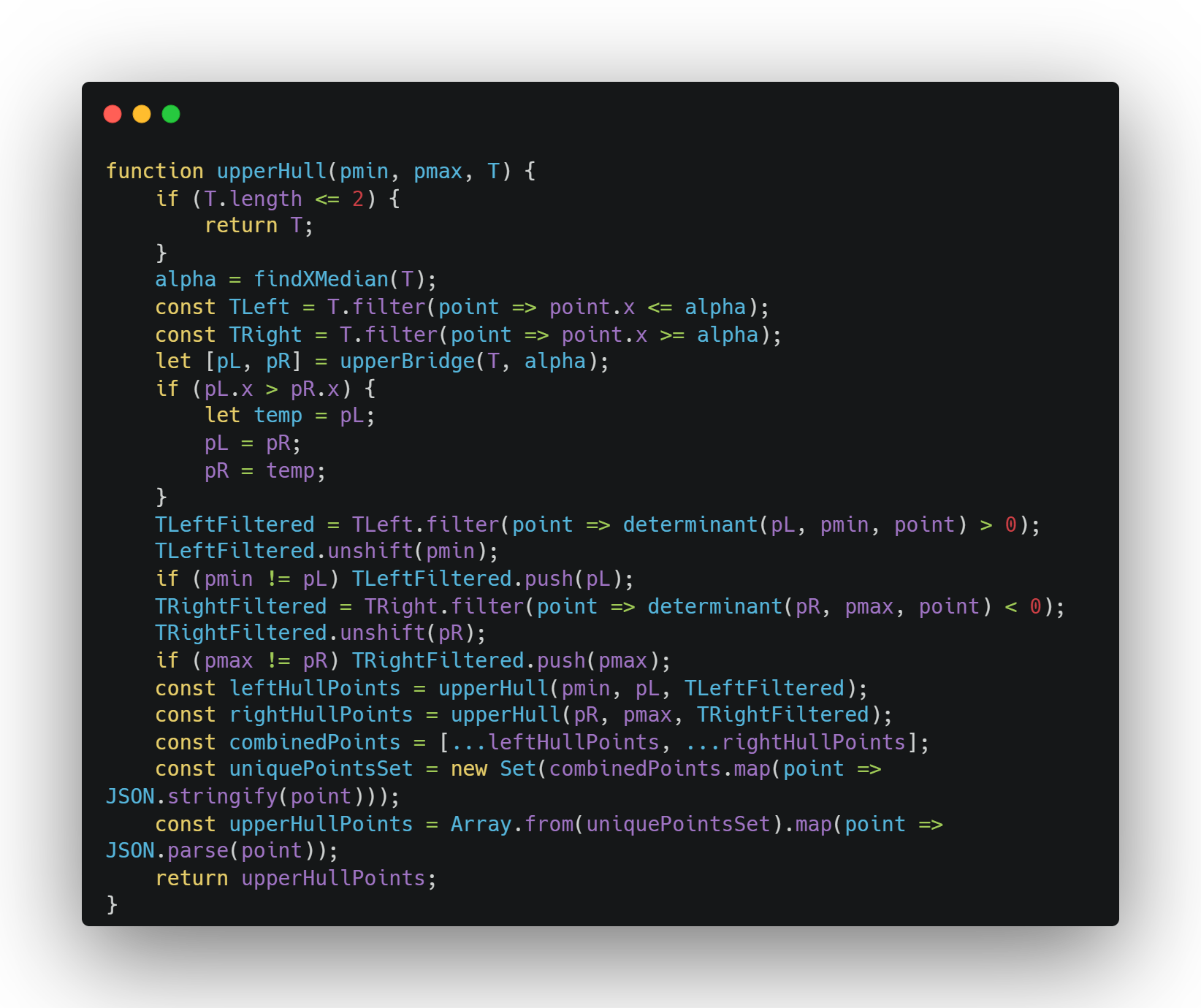
This function is used to recursively find the upperHull for the set of points T. If the passed parameter has 2 or less points it simply returns T. If not: It finds the median x-coordinate of the set.It then partitions the set into TLeft and TRight by comparing their x-coordinates with the median.It calls upperBridge to find the upper edge (pL, pR) of the hull for the left and right subsets.It filters the left and right subsets to remove points that lie below the line segments formed by pmin, pL, and pmax, pR, respectively.It recursively calls upperHull for the left and right subsets with the filtered points and the corresponding upper edge points.It combines the points from both recursive calls, removes duplicates, and returns the upper hull points.
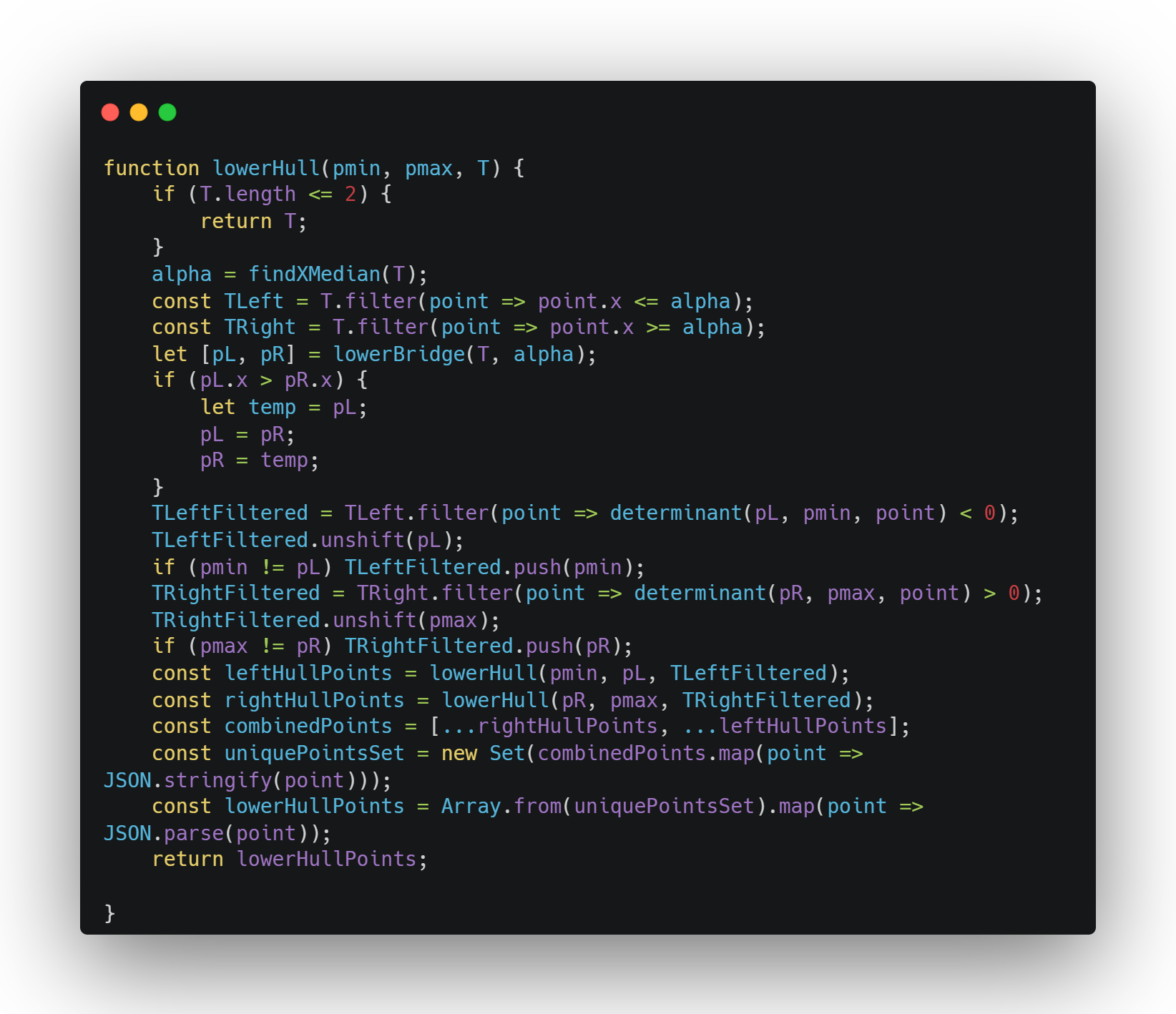
Lower Hull Function
This function is used to recursively find the lowerHull for the set of points T. If the passed parameter has 2 or less points it simply returns T. If not: It finds the median x-coordinate of the set.It then partitions the set into TLeft and TRight by comparing their x-coordinates with the median.It calls lowerBridge to find the lower edge (pL, pR) of the hull for the left and right subsets.It filters the left and right subsets to remove points that lie above the line segments formed by pmin, pL, and pmax, pR, respectively.It recursively calls lowerHull for the left and right subsets with the filtered points and the corresponding lower edge points.It combines the points from both recursive calls, removes duplicates, and returns the lower hull points.
Upper Bridge Function
This function is used to find an upperBridge for the set of points S and alpha is the median x-coordinate If the set had 2 or less points it just returns S. If not: It randomly creates pairs of the points in S and calculates the slopes for each line segment pair. It then finds the median slope among the non-vertical line segments and categorizes the line segment pairs into the lists Small,Equal and Large based on their slopes relative to the slopeMedian. It finds the point with the maximum y-intercept among all line segments whose slopes are equal to or greater than slopeMedian.It identifies a point with maximum x-coordinate(pm) and point with minimum x-coordinate(pk) on the line identified in the previous step and Based on the positions of pm, pk, and alpha, it selects candidate points for further processing. This is done as follows:
If pm.x > alpha and pk.x <= alpha , then both pk and pm are likely on the upper hull and are returned directly. However, If pm.x <=alpha, it indicates the maximum y-intercept line might be entirely to the left of the median. In this case: for points (Pi,Pj) belonging to Small add all the points to candidates but for points(Pi,Pj) belonging to (Large U Equal) add only Pj to candidates. Similarly: If pk.x> alpha, it indicates the maximum y-intercept line might be entirely to the right of the median. In this case: for points (Pi,Pj) belonging to Large, add all the points to candidates but for points (Pi,Pj) belonging to (Small U Equal) add only Pi to candidates.
Finally, It recursively calls upperBridge with the candidate points to refine the upper edge until it finds the appropriate pL and pR.

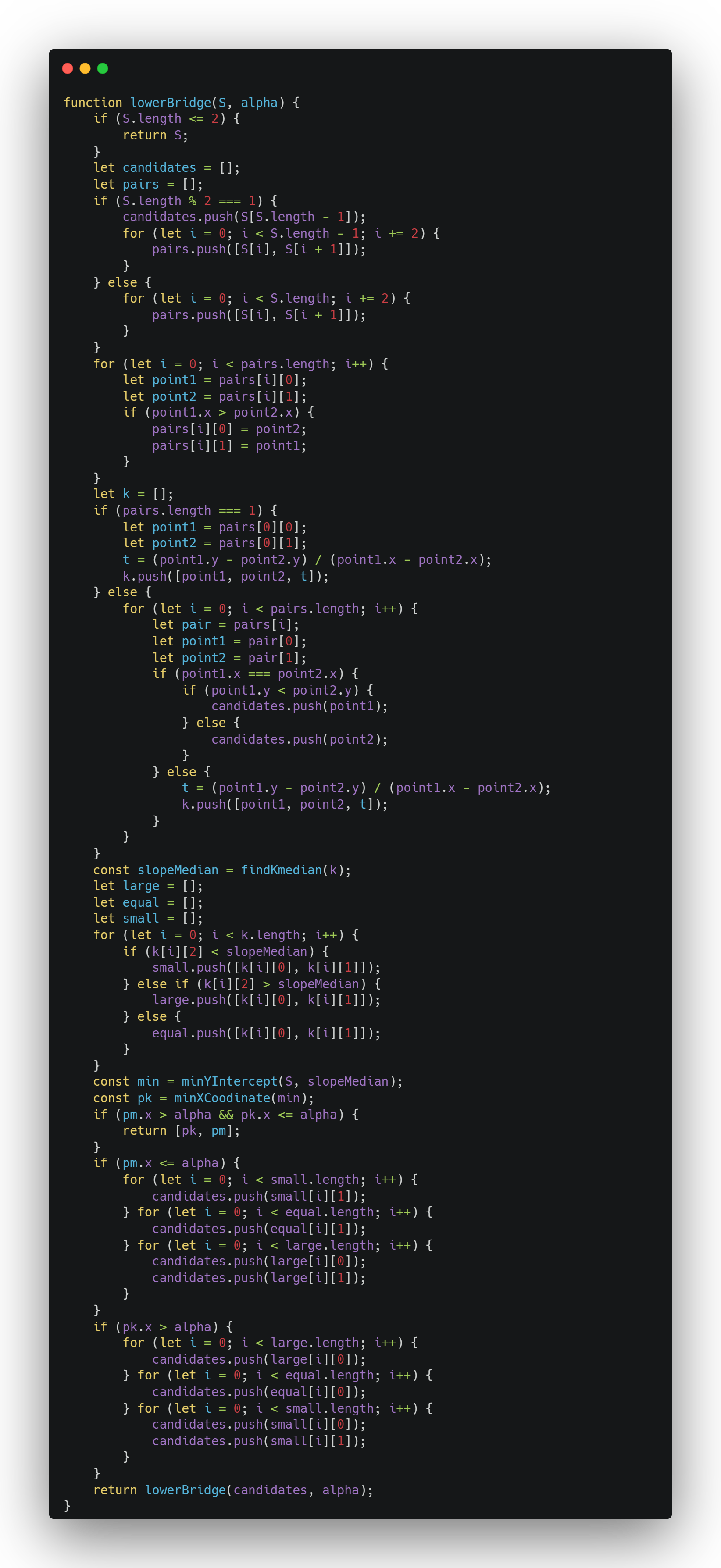
Lower Bridge Function
This function is used to find an lowerBridge for the set of points S and alpha is the median x-coordinate
If the set had 2 or less points it just returns S.
If not:
It randomly creates pairs of the points in S and calculates the slopes for each line segment pair.
It then finds the median slope among the non-vertical line segments and categorizes the line segment pairs into the
lists Small,Equal and Large based on their slopes relative to the slopeMedian.
It finds the point with the minimum y-intercept among all line segments whose slopes are equal to or lesser than
slopeMedian.It identifies a point with maximum x-coordinate(pm) and point with minimum x-coordinate(pk) on the line
identified in the previous step and Based on the positions of pm, pk, and alpha, it selects candidate points for further
processing.
This is done as follows:
If pm.x > alpha and pk.x <= alpha , then both pk and pm are likely on the upper hull and are returned directly. However,
If pm.x <=alpha, it indicates the maximum y-intercept line might be entirely to the left of the median. In this
case: for points (Pi,Pj) belonging to Large add all the points to candidates but for points(Pi,Pj) belonging to
(Small U Equal) add only Pj to candidates. Similarly: If pk.x> alpha, it indicates the maximum y-intercept line
might be entirely to the right of the median. In this case: for points (Pi,Pj) belonging to Small, add all the
points to candidates but for points (Pi,Pj) belonging to (Large U Equal) add only Pi to candidates.
Finally, It recursively calls lowerBridge with the candidate points to refine the lower edge until it finds the appropriate pL and pR.